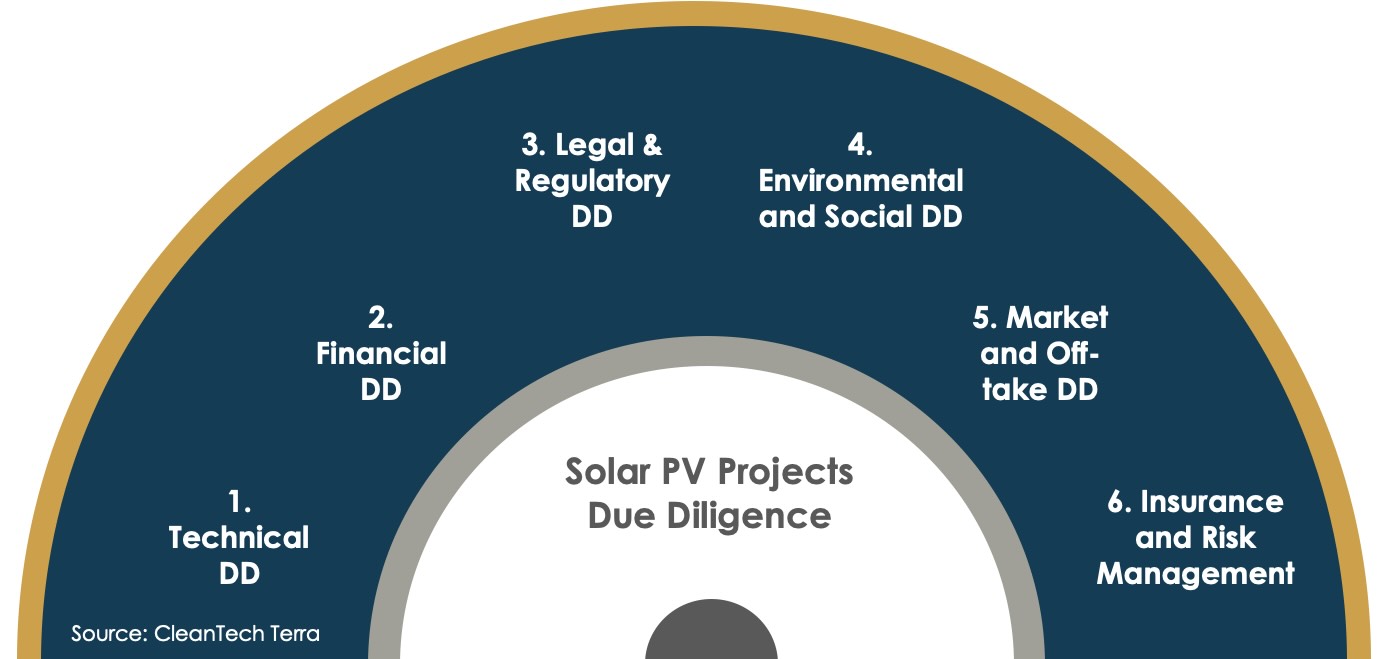
Solar PV
Implementing solar photovoltaic (PV) systems in the commercial and industrial (C&I) sector involves navigating a series of complex challenges. One of the primary considerations is site assessment and system design. Businesses must determine the optimal size and configuration of the solar PV system based on their energy consumption patterns, available space for solar panels, and site-specific solar irradiance. This requires a detailed analysis to ensure maximum energy production and cost-effectiveness.
Another challenge lies in the integration of solar PV with existing electrical infrastructure. Companies need to ensure that the solar system is compatible with their current energy setup, which may include integration with the grid, existing renewable energy sources, or energy storage systems. This integration must be seamless to ensure energy reliability and efficiency, and to maximize the benefits of solar energy.
In addition to technical considerations, regulatory and permitting processes can pose significant hurdles. Navigating local building codes, electrical standards, and zoning regulations is crucial for the legal and safe installation of solar PV systems. Moreover, businesses must often engage in a lengthy and complex process to secure the necessary permits and approvals for construction and operation.
Financial aspects of solar PV implementation are also a key concern. Companies must evaluate the cost of installation, potential savings on energy bills, available government incentives or subsidies, and the expected return on investment. Balancing these financial considerations with the long-term sustainability and environmental benefits of solar energy is critical for decision-making.
Lastly, maintaining and monitoring the solar PV system to ensure optimal performance over its lifespan is a challenge that requires ongoing attention. This includes regular maintenance, performance monitoring, and potentially troubleshooting and repairs, which necessitates a comprehensive understanding of solar PV technology and system management.
Overall, implementing solar PV in the C&I sector demands a comprehensive approach that addresses site-specific considerations, technical integration, regulatory compliance, financial analysis, and long-term maintenance and monitoring. It requires expert knowledge and careful planning to ensure the successful and sustainable adoption of solar energy solutions.
Wind
Integrating wind energy solutions in the commercial and industrial (C&I) sector is fraught with unique challenges. For companies contemplating wind energy projects, the primary hurdle is often the site-specific nature of wind power. Wind energy feasibility heavily depends on local wind patterns, which necessitates detailed wind resource assessments to ensure viable and efficient energy generation. This process involves sophisticated analysis to predict long-term wind speeds and patterns, essential for calculating potential energy yield and project viability.
Moreover, the installation of wind turbines in C&I environments must be carefully planned to minimize impact on existing operations and local communities. This includes considering the physical footprint of turbines, noise levels, and visual impacts, which can be significant concerns in densely populated or sensitive areas. The height and type of turbines chosen must align with both the wind resource characteristics and the constraints of the site.
The integration of wind energy with existing power systems presents another set of challenges. Ensuring that the intermittent nature of wind energy harmonizes with a business’s energy demands and grid requirements demands sophisticated energy management and storage solutions. This is critical for maintaining a reliable and consistent power supply, especially in areas with variable wind conditions.
Navigating regulatory and permitting processes is also a complex task. Wind energy projects often face stringent zoning laws, environmental impact assessments, and community consultations. The timeline for obtaining necessary permits and approvals can be lengthy and uncertain, affecting project timelines and costs.
Financial considerations are paramount in wind energy projects. The initial capital investment for wind turbine installation can be substantial, and businesses must evaluate the long-term return on investment. This involves analyzing energy cost savings, maintenance costs, potential government incentives, and the lifespan of the wind turbines.
In conclusion, implementing wind energy in the C&I sector requires a multifaceted approach that addresses site-specific wind resources, installation challenges, regulatory compliance, and financial feasibility. It demands a combination of technical expertise, strategic planning, and a deep understanding of the specific energy needs and constraints of each business.
Energy Storage
Implementing Energy Storage Systems (ESS) in the commercial and industrial (C&I) sector is a complex and challenging endeavor. For businesses looking to integrate ESS, the primary challenge lies in accurately determining their specific energy storage needs. This involves assessing energy consumption patterns, peak demand periods, and potential cost savings, which requires a deep understanding of the business’s operational dynamics and energy usage.
Moreover, the integration of ESS must be strategically planned to ensure compatibility with existing energy systems, whether they are connected to the grid, renewable energy sources like solar or wind, or a hybrid setup. This compatibility is crucial for maximizing efficiency and achieving the desired energy management goals, such as reducing peak demand charges, providing backup power, or optimizing renewable energy use.
The choice of technology and capacity of the energy storage system is another critical factor. Businesses must navigate a rapidly evolving landscape of battery technologies and energy management systems, each with its own set of advantages, limitations, and cost implications. Deciding between high-capacity, long-duration storage versus more compact, short-duration solutions depends on the specific energy objectives and financial constraints of the business.
Additionally, navigating regulatory frameworks and incentive programs can be daunting, as they vary by region and are subject to change. Compliance with safety standards and environmental regulations is also essential to ensure the longevity and legality of the ESS installation.
Finally, the financial investment required for ESS is significant, and businesses must evaluate the return on investment, taking into account potential energy cost savings, incentives, and the lifespan of the storage system. This requires a comprehensive financial analysis to ensure the viability and sustainability of the ESS project.
In summary, planning and implementing Energy Storage Systems in the C&I sector is a multifaceted process that demands technical expertise, strategic planning, and a thorough understanding of the specific energy needs and financial considerations of each business.
EV Charging
Planning the electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure for the commercial and industrial (C&I) sector presents a unique set of challenges. For companies and gas stations looking to integrate EV charging solutions, the task requires a careful balancing act. Firstly, there is the need to predict future EV adoption rates and charging demands, which can be a moving target as EV technology and market penetration evolve. This makes it crucial to design a scalable and adaptable infrastructure. Additionally, the placement and type of chargers need to be strategically thought out to maximize accessibility and convenience, while minimizing disruption to existing operations.
Furthermore, integrating EV charging infrastructure often involves navigating complex electrical grid requirements and local regulations, which can vary widely and change frequently. Companies must also consider the potential impact on their existing electrical systems and ensure they can handle the increased load without compromising safety or reliability.
Lastly, the financial aspects pose their own challenges. Determining the most cost-effective approach, whether it’s investing in fast-charging technology or opting for a larger number of slower, more affordable chargers, requires a nuanced understanding of both the current market and future trends. This is alongside the considerations for potential revenue streams, such as charging fees or partnerships with EV manufacturers or energy providers.
In essence, planning for EV charging infrastructure in the C&I sector is a complex, multifaceted endeavor that demands expertise, forward-thinking, and a tailored approach to meet the specific needs of each business or location.